Gulf War-era veterans now account for the largest share of all U.S. veterans. In 2018, about 7% of U.S. adults were veterans, down from 18% in 1980, according to the Census Bureau. This drop coincides with decreases in active-duty personnel.
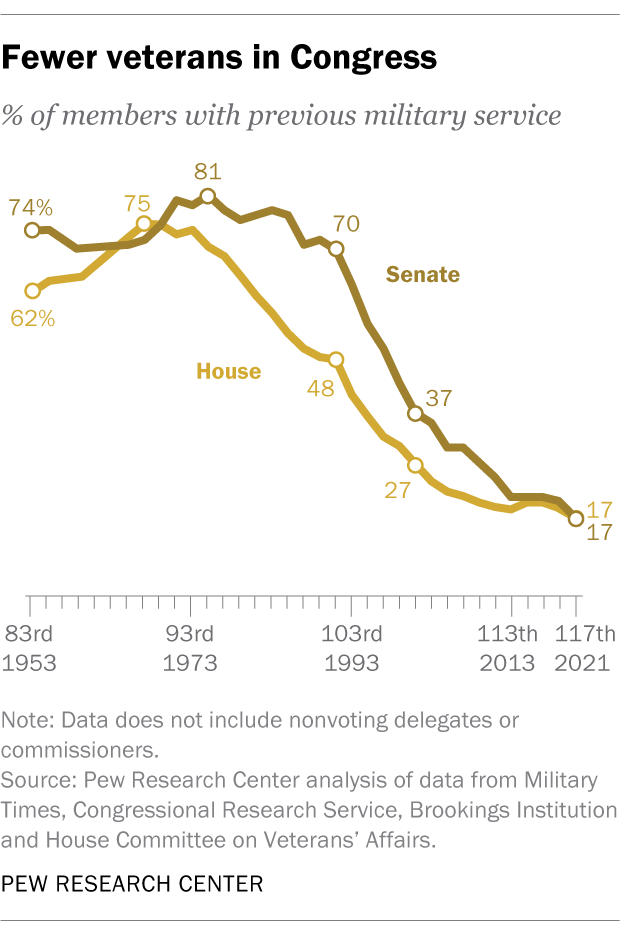
By 2046, the department estimates there will be around 12.5 million veterans, a decrease of about 35% from current numbers. Currently, about nine-in-ten veterans are men, while about one-in-ten are women, according to the VA’s 2021 population model estimates. By 2046, the share of female veterans is expected to increase to about 18%. As the share of Americans who are veterans has declined, so has the share of legislators who have previously served in the military. In the current Congress, 17% of lawmakers in both houses have prior military service, down drastically from just a few decades ago.
Projections also indicate that the veteran population will become slightly younger, with 33% of veterans being younger than 50 in 2046 compared with 27% in 2021, even as the overall U.S. population continues to age.